On a smooth plane surface (figure) two block $A$ and $B$ are accelerated up by applying a force $15\, N$ on $A$. If mass of $B$ is twice that of $A$, the force on $B$ is ........... $N$
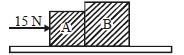
On a smooth plane surface (figure) two block $A$ and $B$ are accelerated up by applying a force $15\, N$ on $A$. If mass of $B$ is twice that of $A$, the force on $B$ is ........... $N$

- [AIIMS 2012]
- A
$30$
- B
$15$
- C
$10$
- D
$5$
Similar Questions
A block of mass $m$ is placed on a smooth inclined wedge $ABC$ of inclination $\theta$ as shown in the figure. The wedge is given an acceleration $a$ towards the right. The relation between $a$ and $\theta$ for the block to remain stationary on the wedge is
A block of mass $m$ is placed on a smooth inclined wedge $ABC$ of inclination $\theta$ as shown in the figure. The wedge is given an acceleration $a$ towards the right. The relation between $a$ and $\theta$ for the block to remain stationary on the wedge is
- [NEET 2018]
In the figure shown $'P'$ is a plate on which a wedge $B$ is placed and on $B$ a block $A$ of mass $m$ is placed. The plate is suddenly removed and system of $B$ and $A$ is allowed to fall under gravity. Neglecting any force due to air on $A$ and $B$, the normal force on $A$ due to $B$ is
In the figure shown $'P'$ is a plate on which a wedge $B$ is placed and on $B$ a block $A$ of mass $m$ is placed. The plate is suddenly removed and system of $B$ and $A$ is allowed to fall under gravity. Neglecting any force due to air on $A$ and $B$, the normal force on $A$ due to $B$ is
A horizontal force $10 \mathrm{~N}$ is applied to a block $A$ as shown in figure. The mass of blocks $A$ and $B$ are $2 \mathrm{~kg}$ and $3 \mathrm{~kg}$ respectively. The blocks slide over a frictionless surface. The force exerted by block $A$ on block $B$ is :
A horizontal force $10 \mathrm{~N}$ is applied to a block $A$ as shown in figure. The mass of blocks $A$ and $B$ are $2 \mathrm{~kg}$ and $3 \mathrm{~kg}$ respectively. The blocks slide over a frictionless surface. The force exerted by block $A$ on block $B$ is :
- [NEET 2024]
A wooden block of mass $2\; kg$ rests on a soft horizontal floor. When an iron cylinder of mass $25\; kg$ is placed on top of the block, the floor yields steadily and the block and the cylinder together go down with an acceleration of $0.1\; m /s^2$. What is the action of the block on the floor $(a)$ before and $(b)$ after the floor yields ? Take $g = 10 \;m /s^2$. Identify the action-reaction pairs in the problem
A wooden block of mass $2\; kg$ rests on a soft horizontal floor. When an iron cylinder of mass $25\; kg$ is placed on top of the block, the floor yields steadily and the block and the cylinder together go down with an acceleration of $0.1\; m /s^2$. What is the action of the block on the floor $(a)$ before and $(b)$ after the floor yields ? Take $g = 10 \;m /s^2$. Identify the action-reaction pairs in the problem
A constant force $F$ is applied in horizontal direction as shown in figure. Contact force between $M$ and $m$ is $N$ and between $m$ and $M'$ is $N'$ then
A constant force $F$ is applied in horizontal direction as shown in figure. Contact force between $M$ and $m$ is $N$ and between $m$ and $M'$ is $N'$ then
